|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Brain Structure in this note refer specifically to the structure of Human brain. It is not general term applies to all animals. There are some animals that does not have brain (even though they have their own nervous system). There are a lot of animal species that has brain but the detailed structure of them are different among species. In this note, I would like to focus on Human brain structure since my main intereste lies in human neurosience more specifically in understanding myself. However it is not the purpose (and out of my capability) to describe the full details of human brain like the Brain Anatomy text book in medical school. It is not possible for me to dig into that far since I have never been trained in medical school, but plan to provide information bare enough to understand technical articles / watch lectures on YouTube.. and (hopefully) be enough for those exposed to basic anatomy in biology course.
Why I don't like Anatomy ? and How to get it over ?There might be some people who likes Anatomy and memorize all the name of all those names to the very tiny parts at the corner without much difficulties and stress. But unfortunately I am not that type of person and a lot of readers would be similar type as I am. I started thinking of why I don't like it and came out with a few reasons :
Unfortunately I don't have any one shot solution for any of these. Especially for the first item, I didn't even try to find the solution because I know there is no clear solution for it. But I think there would at least something to try for the second one. It is to make my own word book for Latin and Greek try to remorize it whenever I see those words from the labels on the pictures in Anatomy books. I would not recommend you to write down hundreds of Latin/Greek words and try to remember it by rote memory. Just put those words in your notebook whenever you see the new words and try to check on the meaning of the words in Latin/Greek dictionary. Some references under Dictionary section may help you with this. One good thing for this and building a Greek/Latin vacabulary in your memory would help you not only anantomy but also for other subjects (like biology, organic chemistry, biochemistry etc). Why we should study / learn on Brain Anatomy ?If you are not a big fan of Anatomy, you would have ask this to yourself many times and try to avoid looking into brain anatomy even though you are strongly interested in neuroscience / brain science. Personally I am not a big fan of anatomy and extremely poor at anything that requires a certain degree of rote memory. so I asked the same questions over and over to myself. Unfortunately I haven't found any way / reason to avoid studying brain anatomy to study about neuroscience / brain science. A few reasons why I should study on the anatomy are listed below :
In short, regardless of whether you like or not, a certain level knowledge of brain anatomy is a mandate and you cannot avoid it. How to study/learn on Brain Anatomy ?If you are a student in medical program, there wouldn't be much thing I can advise or propose mainly because there wouldn't be much options except just following whatever you are asked to do in your program. To be honest, I don't think the way you are asked to do in most of school program is the best and the most efficient way to learn anything, but it may be good enough to memorize many things in relatively short period. (I don't know how long you can maintain/retain the memory after the end of the course). I don't think the way we are being tought or trained at school is the best/efficient way in terms of neurocience / educational psychology. Interestingly even the educational program about neuroscience does not seem to go in such a way that is suggested to be efficient in the theory/research of neuroscience/educational psychology. My personal way of learning / memorizing about brain anatomy is as follows. I don't know if this is the best way, but it seems the best fit for myself and I don't feel any stress about this. I have extremly poor memory and I extremly hate the process of rote memorization. But doing this way, I see myself getting rapidly familiar with the overal brain anatomy without getting any stress. Of course, I am not at the expert level in this area, but I think I reached pretty good position as an hobbiest.
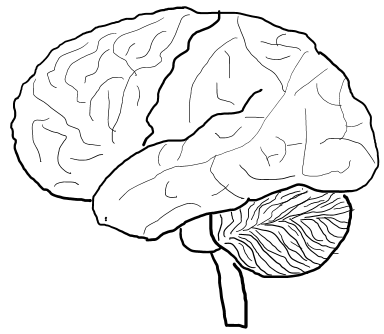
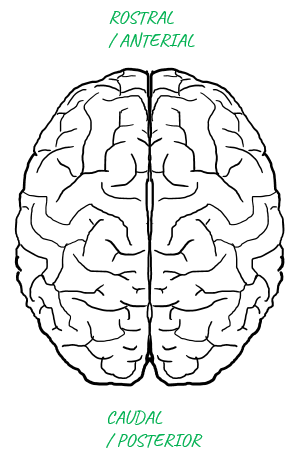
Do you know how the brain placed inside the skull ?I think everybody would have seen a picture of a human brain as shown below. Do you know which is front (the part right inside your forehead) and which is back (the part right inside your backhead) ? Don't be disappointed if you don't know. I myself had been confused for a long, long time. Sometimes I put the labels on the picture indicating 'front' and 'back', but soon get confused again if I see the picture with no label.
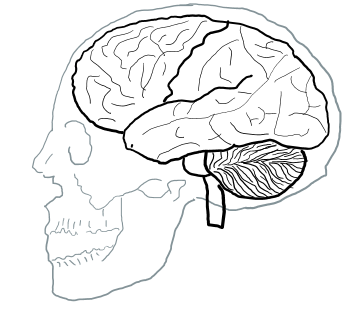
Finally I found my own trick to remember the front and back of the brain image. It is to get the picture (or drawing it in your own would be even better) with skull as shown below. You don't even label the front and back. Just imprint this image in your brain (memory) as a picture and recall this image whenever you get confused.
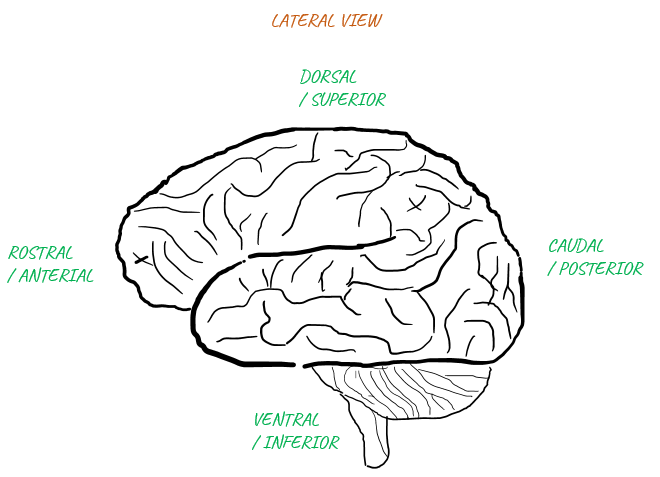
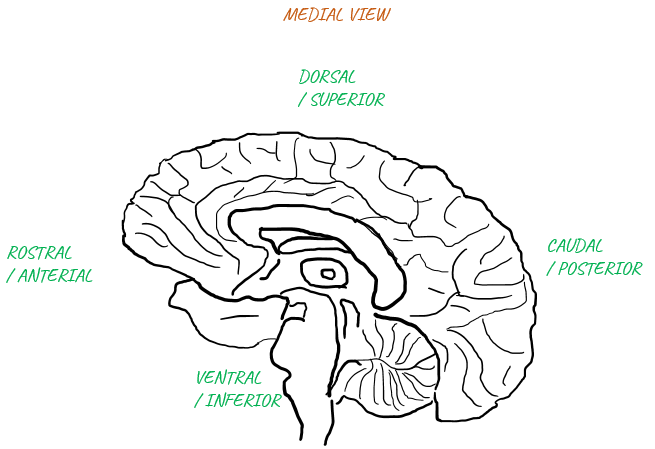
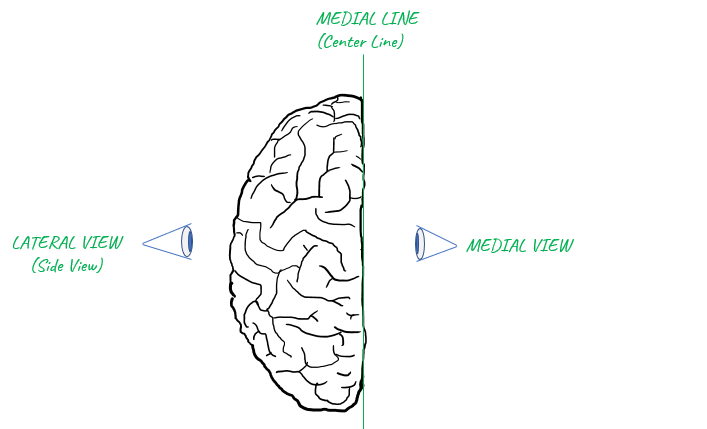
Vocabularies for DirectionsI think the first thing that we should be familiar with would be a list of words indicating the directions since those words would pop up in almost every basic materials (articles, lectures etc). Again.. most of the words for the direction are also Greek/Latin based. A short list of those words representing the directions are listed below.
Applying these words to the highest level brain structre is as follows : Just try to remember the whole image with label in your brain until you can recall these images automatically whenever you see those words.
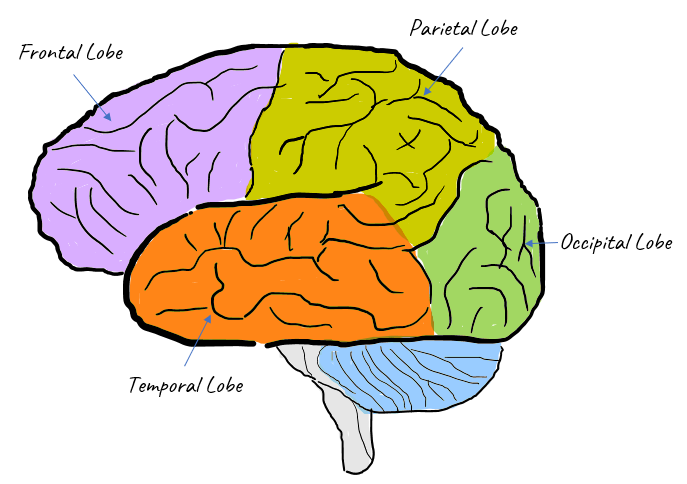
Structure of Cerebral CortexProbably one of the most important picture that you should be familiar with would be this. The cerebral cortex(surface) of our brain can be divided into several import area as shown below. Whatever texts or video you would read/watch about neuroscience, you would see at least one of the names (labels) shown here.
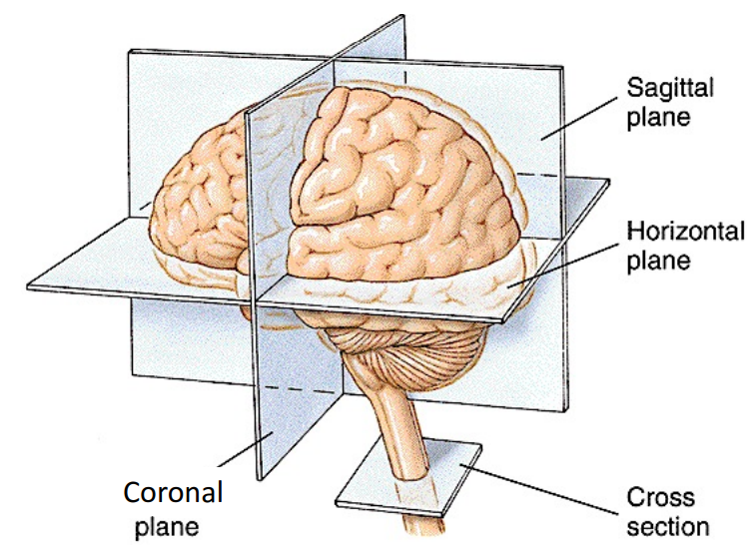
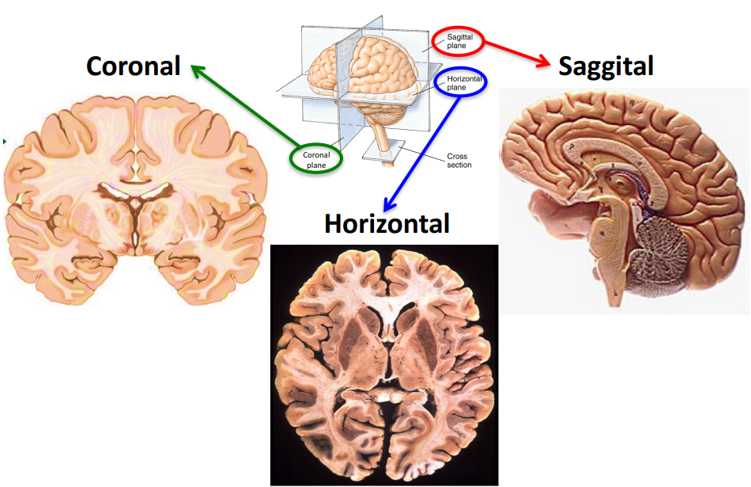
Planar / Sectional View of the BrainUntill we have hologram as our everyday display, we would need to rely on represending everything (the brain as well) in 2 dimensional display. Even it the computer display and text book drawing some 3D objects it is still the prjection of the 3D object onto 2D plane, not real 3D. One common way is to help you to get an idea of a 3D object in 2D display is to cut through the 3D object with various 2D plane and let your brain to imagine it in 3D in your brain. Unlike other parts of nervous system (e.g, spinal cord, peripheral nerves etc), brain is a bulky 3D object with very complicated internal structure. We would need to cut through it in various different angles to get the full picture. So it has been a long practice to get the image of a cut-through image by anatomoy or by brain imaging (e.g, MRI, CT, fMRI) and you would need quite a lot of practice to interpret those cut-through images in the context of 3D brain. A few of the most frequently used cut-through plane are shown as below. You may have seen such a description like "this is sagittal section of the brain" or "this is coronal section of the brain" etc.
Image Source : LEC 1A - Anatomy Of The Nervous System Following is an example of the sectional image with Coronal, Sggital, Horizontal plane. You may need to quite a lot of practice to identify a certan part of brain region (e.g, hypothalmus or hippocampus etc) in each sectional image. For example, some of the region would be seen only in a specific section, not in other sections.
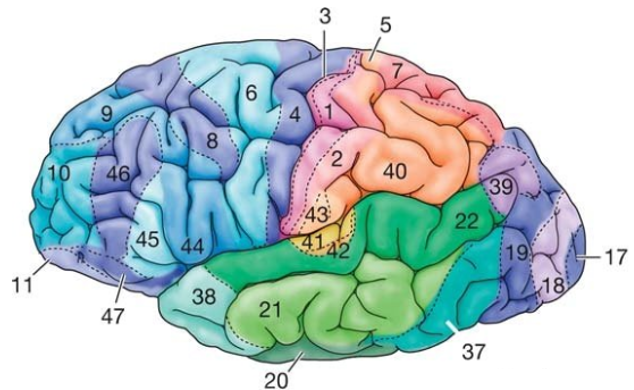
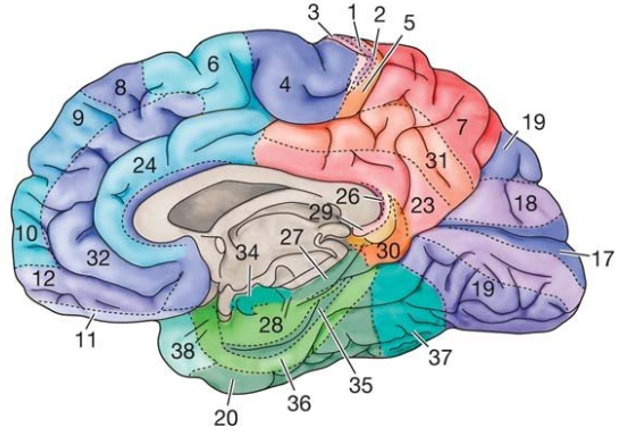
Image Source : LEC 1A - Anatomy Of The Nervous System Brodmann's MapI think you may have seen most of the drawings / pictures in previous sections when you are reading / studying neuroscience as an hobbiest. However there wouldn't be many cases where you see a little bit more detailed classification of brain reason as shown below. This is called Brodmann's map naming after the scientist who created this map. If you can figure out a reason just by looking at the numbers in other text and lecture or at least know what the number mean and find out any document showing the details, you would consider yourself as pretty experienced in neuroscience. I am not expecting you to memorize all the details of this map. It would be enough if you know what to look for when you see the comments like 'Broadmann map 17' or just the number 17.
Image Source : Hallucinations Experienced by Visually Impaired: Charles Bonnet Syndrome (ResearchGate) This is the table with the name/label for each of the numbered area shown in the map showing a little bit of description.
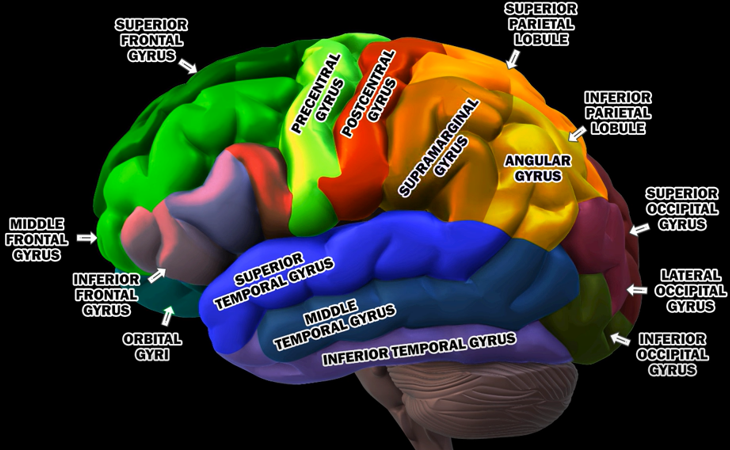
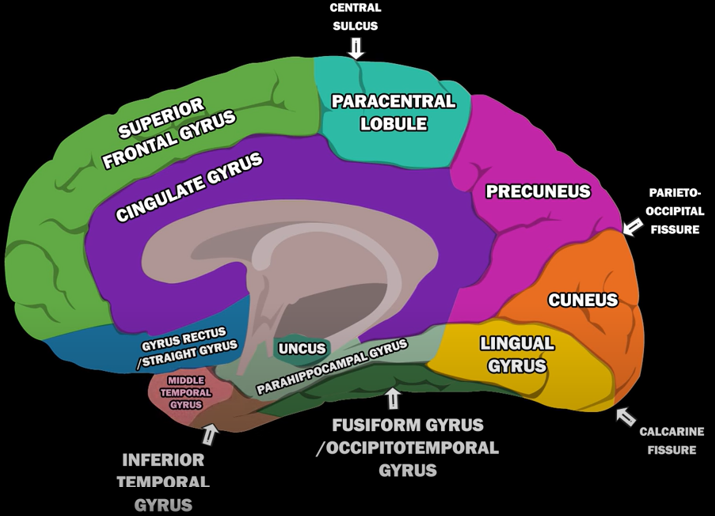
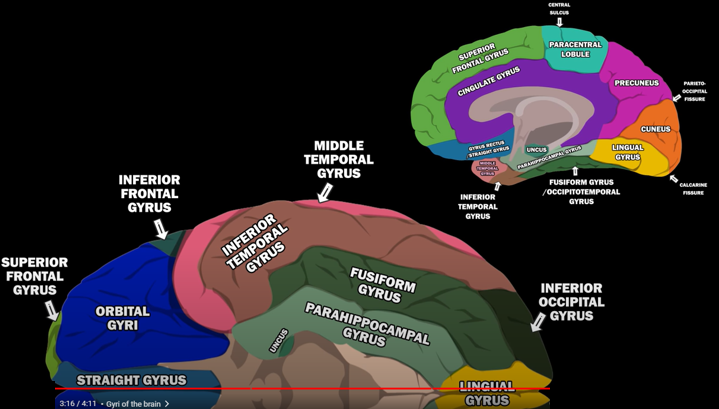
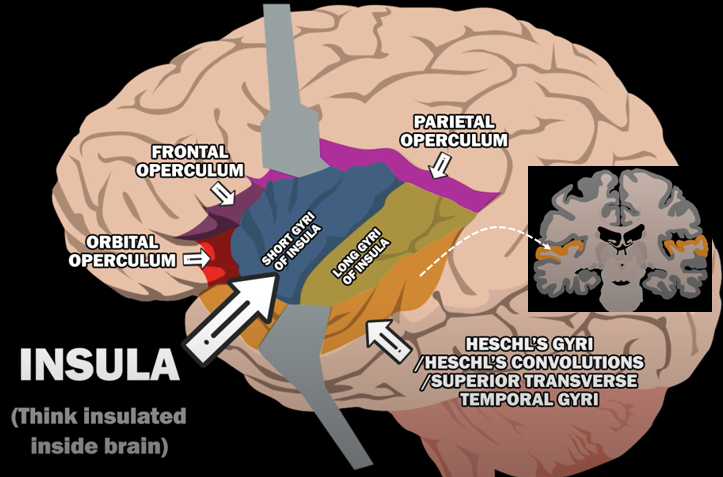
Gyri of Human BrainThe human brain is a marvel of intricate folds and ridges, and gyri are the prominent ridges that give it this characteristic appearance. These convolutions are not merely aesthetic; they significantly increase the brain's surface area, allowing for a greater density of neurons and enhanced cognitive function within the confines of the skull. Gyri play a crucial role in various brain functions, with specific gyri often specializing in particular tasks, such as processing sensory information, controlling motor movements, or contributing to language and memory. Understanding the structure and function of gyri is essential for unraveling the complexities of the human brain and its remarkable capabilities. Followings are the list of well defined Gyri in human brain
For the specific location of each gyri, refer to the YouTube snapshots shown below (I would suggest you to watch the original YouTube as well)
Image Source : GYRI OF THE BRAIN - LEARN IN 4 MINUTES
Image Source : GYRI OF THE BRAIN - LEARN IN 4 MINUTES
Image Source : GYRI OF THE BRAIN - LEARN IN 4 MINUTES
Image Source : GYRI OF THE BRAIN - LEARN IN 4 MINUTES
Reference
Neuro Anatomy Web Tools
YouTube
Dictionary
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||