|
NR CORE - UDM
UDM stands for Unified Data Management. As the name implies it is a function/service that manges Data. What kind of data it manages ? It is user data (i.e, data of subscribers). In 4G, HSS played this role.. but in 5G, the HSS role split into two different services : UDM and AUSF. AUSF is mainly for Authentication Process and UDM is managing the user data for all other process. As shown in the illustration below, UDM is interfaced with many other services : AUSF, AMF, SMF, SMSF.
It means when AUSF, AMF, SMF, SMSF needs subscriber data, it request it to UDM and UDM provide the data to the services that requested.
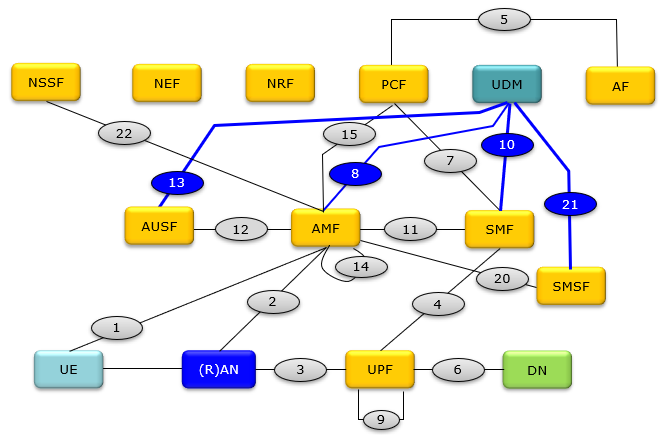
Followings are the name of each network component.
AMF Access and Mobility Management Function ==> Equivalent to MME in 4G
AUSF Authentication Server Function
DN Data Network
NEF Network Exposure Function
NRF Network Repository Function
NSSF Network Slice Selection Function
PCF Policy Control Function ==> Equivalent to PCRF in 5G
(R)AN (Radio) Access Network
SMF Session Management Function
UDM Unified Data Management ==> Equivalent to HSS in 4G
UPF User Plane Function ==> Equivalent to PGW in 4G
SMSF SMS Function
SEAF SEcurity Anchor Function ==> part of AMF function
ARPF Authentication credential Repository and Processing Function
SIDF Subscription Identifier De-concealing Function
Inter play between UDM and Other Components
Even though the illustrations shown above indicates the interplay beween UDM and other components, I think following diagram shows better with focus on UDM.
< 29.503-Figure 4.1-1: Reference model UDM >
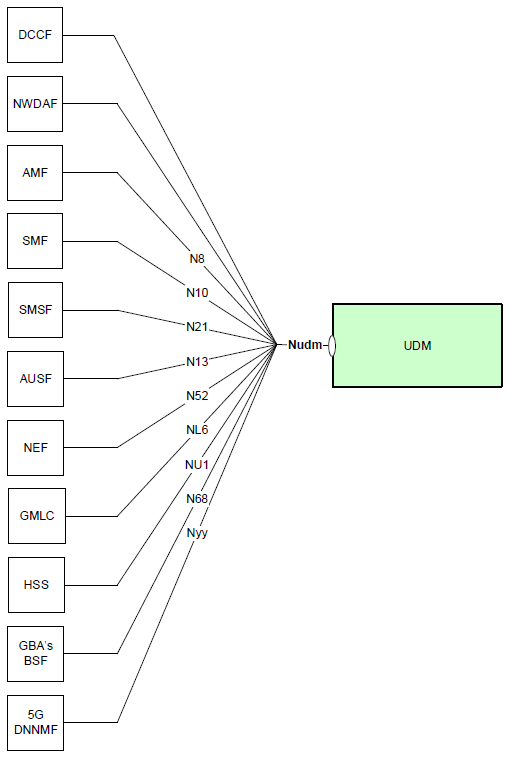
Here goes a short descriptions for each of the interactions between UDM and other network components depicted on the diagram.
-
DCCF (Data Collection Configuration Function): Interacts with UDM to configure how user data is collected for various services.
-
NWDAF (Network Data Analytics Function): Exchanges analytics data with UDM to optimize network performance and user experience.
-
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function): Coordinates with UDM for authentication and to maintain user profiles for mobility management.
-
SMF (Session Management Function): Works with UDM to manage sessions and user data related to connectivity and service access.
-
SMSF (Short Message Service Function): Relies on UDM for storing and retrieving SMS-related user data.
-
AUSF (Authentication Server Function): Verifies user credentials with UDM during the authentication process.
-
NEF (Network Exposure Function): Utilizes UDM to control user data exposure to external network functions.
-
GMLC (Gateway Mobile Location Centre): Accesses location-related user data from UDM for services requiring location information.
-
HSS (Home Subscriber Server): Legacy function from 4G that interacts with UDM for subscriber data management in the transition to 5G.
-
GBA's BSF (Generic Bootstrapping Architecture's Bootstrapping Server Function): Uses UDM for secure user data exchange in bootstrapping procedures.
-
5G DNNMF (5G Dynamic Network Node Management Function): Potentially a custom or proprietary function interacting with UDM for dynamic network management and configuration.
UDM Functionality
Based on 23.501-6.2.7, the functionality of UDM is descrbed as follows.
- Generation of 3GPP AKA Authentication Credentials.
- User Identification Handling (e.g. storage and management of SUPI for each subscriber in the 5G system).
- Support of de-concealment of privacy-protected subscription identifier (SUCI).
- Access authorization based on subscription data (e.g. roaming restrictions).
- UE's Serving NF Registration Management (e.g. storing serving AMF for UE, storing serving SMF for UE's PDU Session).
- Support to service/session continuity e.g. by keeping SMF/DNN assignment of ongoing sessions.
- MT-SMS delivery support.
- Lawful Intercept Functionality (especially in outbound roaming case where UDM is the only point of contact for LI).
- Subscription management.
- SMS management.
- 5G-VN group management handling.
- Support of external parameter provisioning (Expected UE Behaviour parameters or Network Configuration parameters).
NOTE 1: The interaction between UDM and HSS, when they are deployed as separate network functions, is defined in TS 23.632 and TS 29.563 or it is implementation specific.
NOTE 2: The UDM is located in the HPLMN of the subscribers it serves, and access the information of the UDR located in the same PLMN
Reference :
|

